DL Destroyer Leader
A flotilla leader was a warship suitable for commanding a flotilla of destroyers or other small warships, typically a small cruiser or a large destroyer (known as a destroyer leader). The flotilla leader provided space, equipment and staff for the flotilla captain, including a wireless room, senior engineering and gunnery officers, and administrative staff to support the officers. They were a feature of navies in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Originally, older light or scout cruisers were often used, but in the early 1900s, the rapidly increasing speed of new destroyer designs meant that such vessels could no longer keep pace with their charges. Accordingly, large destroyer designs were produced for use as leaders.

As destroyers changed from specialized anti-torpedo boat vessels that operated in squadrons to larger multi-purpose ships that operated alone or as leaders of groups of smaller vessels, and as command and control techniques improved (and the technology became more readily available), the need for specialized flotilla leaders decreased and their functions were adopted by all destroyers.Destroyer leader (DL) was a hull classification symbol used by the United States Navy from the 1950s until 1975. These ships were more commonly called frigates, although they were larger than frigates of other navies. They were intended to be larger and more capable than destroyers and to lead a destroyer task force. During the 1975 USN ship reclassification these ships were reclassified as guided missile destroyers (DDG) or guided missile cruisers (CG). A total of 41 ships bore this classification.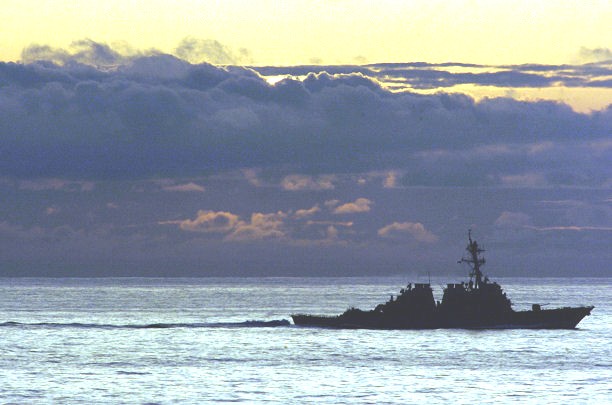
The designations "Cruiser," "Destroyer" and "Frigate" were a source of some confusion in the USN during the 1970s. Existing US carrier escorts were designated as Frigates (DLG and DLGN), but foreign warships of the size of US Frigates were generally classified as destroyers or cruisers. The USN was also applying the term "Patrol Frigate" or "PF" to the much smaller USS Oliver Hazard Perry class of convoy escorts then being designed. This usage was more in line with the "Frigate" designation as used in foreign navies, where it was usually given only to smaller warships of about the same size as the Perrys.

On 30 June 1975, this issue was partially resolved when the following reclassifications were made: Most DLG and DLGN Frigates were redesignated as Guided Missile Cruisers CG and CGN, with these warships retaining their original hull numbers (CG/CGN-16 through 40). Due to their smaller size, the Farragut class missile frigates (DLG-6 through DLG-15) were reclassified as Guided Missile Destroyers and given new hull numbers in that series (DDG-37 through DDG-46). The remaining CLG cruisers that were still active or in reserve were redesignated as CG and retained their existing hull numbers. Existing Guided Missile Escorts (DEG-1 to DEG-6) were redesignated as Guided Missile Frigates (FFG-1 to FFG-6) and those Escorts (DE) still in commission were redesignated as Frigates (FF) and retained their existing hull numbers. USS Oliver Hazard Perry herself was commissioned on 17 December 1977 as FFG-7. This reclassification was incomplete, as the new Ticonderoga class Aegis missile ships were still planned to be designated as Guided Missile Destroyers (DDG-47 class), even though they were much larger vessels than the redesignated conventionally-powered cruisers (ex-DLG, now CG).

Finally, on 1 January 1980, the Ticonderoga class DDGs were redesignated as CGs and Ticonderoga herself was commissioned on 22 January 1983 as CG-47. As the Ticonderoga class retained their originally planned hull numbers, this left a gap in the missile cruiser hull series sequence and hull numbers CG-43 to CG-46 were never assigned to any ship. There was some thought that these unused numbers could be assigned to the new generations of nuclear-powered missile cruisers then being discussed (the revamped CGN-42 and CSGN classes), but none of these were ever built.

This redesignation of the early members of the Ticonderoga class also left a gap in the missile destroyer hull series sequence and hull numbers DDG-47 to DDG-50 were not reassigned to any ship. USS Arleigh Burke, the first of a new class of missile destroyers, was commissioned on 4 July 1991 as DDG-51. Following World War II, many Fletcher (DD-445), Allen M. Sumner (DD-692) and Gearing (DD-710) class destroyers were modified and given new, specialized missions as Fleet Escorts (DDE), radar pickets (DDR) and ASW submarine killers (DDK). The ASW destroyers (DDK) were redesignated as Fleet Escort destroyers (DDE) on 4 March 1950. All Fleet Escort destroyers (DDE) were reclassified as destroyers (DD) on 30 June 1962. Most radar picket destroyers (DDR) were reclassified as destroyers (DD) during the 1960s.

The "DL" designation as originally created on 2 February 1951 meant "Destroyer Leader" and was used to indicate that these warships were significantly larger than those destroyers built during World War II yet still smaller than cruisers. The DL designation was changed to mean "Frigate" on 1 January 1955. When a Terrier missile launcher was added to the design for the planned Farragut DL-6 class, their designation was changed to DLG on 14 November 1956, although none of these ships was actually laid down until the following year. The Mitscher class frigates Mitscher DL-2 and John McCain DL-3 were converted to carry a Tartar missile launcher during the 1960s and were then redesignated as missile destroyers DDG-35 and DDG-36, respectively. As noted above in the cruiser section, on 30 June 1975 most Frigates were redesignated as CG and CGN with the Farragut DLG class being redesignated as missile destroyers DDG-37 through DDG-46.

The designation "DE" was originally assigned to Destroyer Escorts of World War II. It is sometimes stated that "DE" meant "Ocean Escorts" for those convoy escorts of the 1950s-1970s starting with the USS Dealey (DE-1006) class and ending with the USS Knox (DE-1052) class, but this does not appear to have ever been made a formal designation. On 30 June 1975 existing Guided Missile Escorts (DEG) were redesignated as Guided Missile Frigates (FFG) and those Escorts (DE) still in commission were redesignated as Frigates (FF). A number of Edsall (DE-129) class destroyer escorts were converted to Radar Pickets (DER) during the 1950s. They carried that designation during the rest of their careers, although none of them appear to have been used in that role after about 1960. The "PF" designation was originally used for World War II frigtes of the Asheville (PF-1) and Tacoma (PF-3) classes. In the 1970s, it was proposed to designate what became the Oliver Hazard Perry (FFG-7) class as PF which would have then meant "Patrol Frigates."

As for the DDG series, the currently authorized but unnamed DDG-112 of the Arleigh Burke (DDG-51) class is expected to be delivered to the US Navy by December 2010. This may be the last in the original DDG hull series numbers. The DD designation went out of service when USS Cushing DD-995 was decommissioned on 21 September 2005. .



 DLG/CG-27
DLG/CG-27
 USS William H.Standley
USS William H.Standley
 DLG/CG-30
DLG/CG-30
 DLG/CG-24
DLG/CG-24
 USS Vella Gulf
USS Vella Gulf
















 DLG/CG-27
DLG/CG-27 